Explain Different Modes of Spreading Infectious Diseases.
Ask participants if they can briefly say or guess what the terms mean as they relate to transmission of disease. Explain that these terms represent different categories for how infectious diseases are transmitted to people.
Infectious diseases can also be spread indirectly through the air and other mechanisms.

. Pathogens and their vectors can now move further faster and in greater numbers than ever before. Direct contact infections spread when disease-causing microorganisms pass from the infected person to the healthy person via direct physical contact with blood or body fluids. Vertical direct contact transmission occurs when pathogens are transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy birth or breastfeeding.
Explain that understanding how diseases are transmitted is key to knowing how to protect oneself on an infectious. Compare contact vector and vehicle modes of transmission. The Ways Infectious Diseases Spread Infectious diseases can spread in a variety of ways.
Other kinds of direct contact transmission are called horizontal direct contact transmission. Direct transmission and indirect transmission. Airborne droplets from the nose and throat.
The system can better analyze the factors affecting the spread of infectious diseases and provide better theoretical support for the prevention and control of infectious diseases. Direct contact can be categorized as vertical horizontal or droplet transmission. Identify important disease vectors.
Standard precautions are the work practices required to achieve a basic level of infection prevention and control. Through the air from direct or indirect contact with another person soiled objects skin or mucous membrane saliva urine blood and body secretions through sexual contact and through contaminated food and water. The infectious diseases are spread in the following ways.
The primary routes of infectious disease transmission in US. Infections spread by blood and body fluids. Standard precautions are the minimum infection prevention and control practices that must be used at all times for all patients in all situations.
A flu virus can cause a runny nose muscle aches and an upset stomach. However primarily two modes of disease transmission are there. Diseases spread by person-to-person contact Module 6.
Describe the different types of disease reservoirs. Understanding the modes of transmission for an infectious disease is. An infectious agent may be transmitted from its natural reservoir host or environment to a susceptible host in different ways.
The mode of transmission can be direct or indirect. Air sea and land transport networks continue to expand in reach speed of travel and volume of passengers and goods carried. It causes an estimated 219 million cases globally and results in more than 400000 deaths every year.
Examples of direct contact are touching kissing sexual contact contact with oral secretions or contact with body lesions. Healthcare settings are contact droplet and airborne. Many pathogens require a living host to survive while.
Understanding how infectious pathogens spread is critical to preventing infectious disease. Examples of diseases spread by insects and in the examples listed below specifically by mosquitoes. With research on the spread of infectious diseases the advantage of using cellular automata to model complex problems can be used to optimize epidemic models.
Layout of each module. The spreading of any pathogen from one body to another body is termed transmission. Contact transmission can be sub-divided into direct and indirect contact.
Explain the prevalence of nosocomial infections. Direct transmission occurs when the infectious agent is transferred from its reservoir to a susceptible host without an intermediate step. A person with a bacterial infection will often experience redness heat swelling fever and pain at.
These infectious diseases generally spread through contaminated food and water some spread through the transfer of body fluids and skin contact. Three important consequences of global transport network expansion are infectious disease pandemics vector. When an infected person sneezes or coughs the droplets containing the pathogen of diseases such as influenza common.
Direct contact transmission involves the transfer of infectious agents to a susceptible individual through physical contact with an infected individual eg direct skin-to-skin contact. Transmission-based precautions are used when standard. Contact moves germs by.
Moreover the transmission of infections and diseases take place in various ways like it may get transmitted directly or through means of specific bacteria protozoa fungi or virus. They can be caused by either parasites bacteria or viruses. This can occur by direct contact.
11 rows There are two different modes of transmission of diseases. Examples of diseases spread by contact with animals. Touching an infected person or their body fluids such as saliva.
Vector-borne diseases account for more than 17 of all infectious diseases causing more than 700 000 deaths annually. Examples of infectious diseases are Ecoli common cold chickenpox HIV AIDS influenzaflu diphtheria giardiasis infectious mononucleosis malaria dengue tuberculosis etc are some common infectious diseases. How do infections spread.
These diseases are usually spread by contact with an environmental source such as animals insects water or soil. Viruses bacteria parasites or fungi can spread infectious diseases. There are a few general ways that germs travel in healthcare settings through contact ie touching sprays and splashes inhalation and sharps injuries ie when someone is accidentally stuck with a used needle or sharp instrument.
Malaria is a parasitic infection transmitted by Anopheline mosquitoes. Infections spread by animals and insects and less common infectious diseases Module 5. Infections spread by sexual contact and blood and body fluids.
Direct Transmission This occurs. Infections spread by sexual contact and Part II.
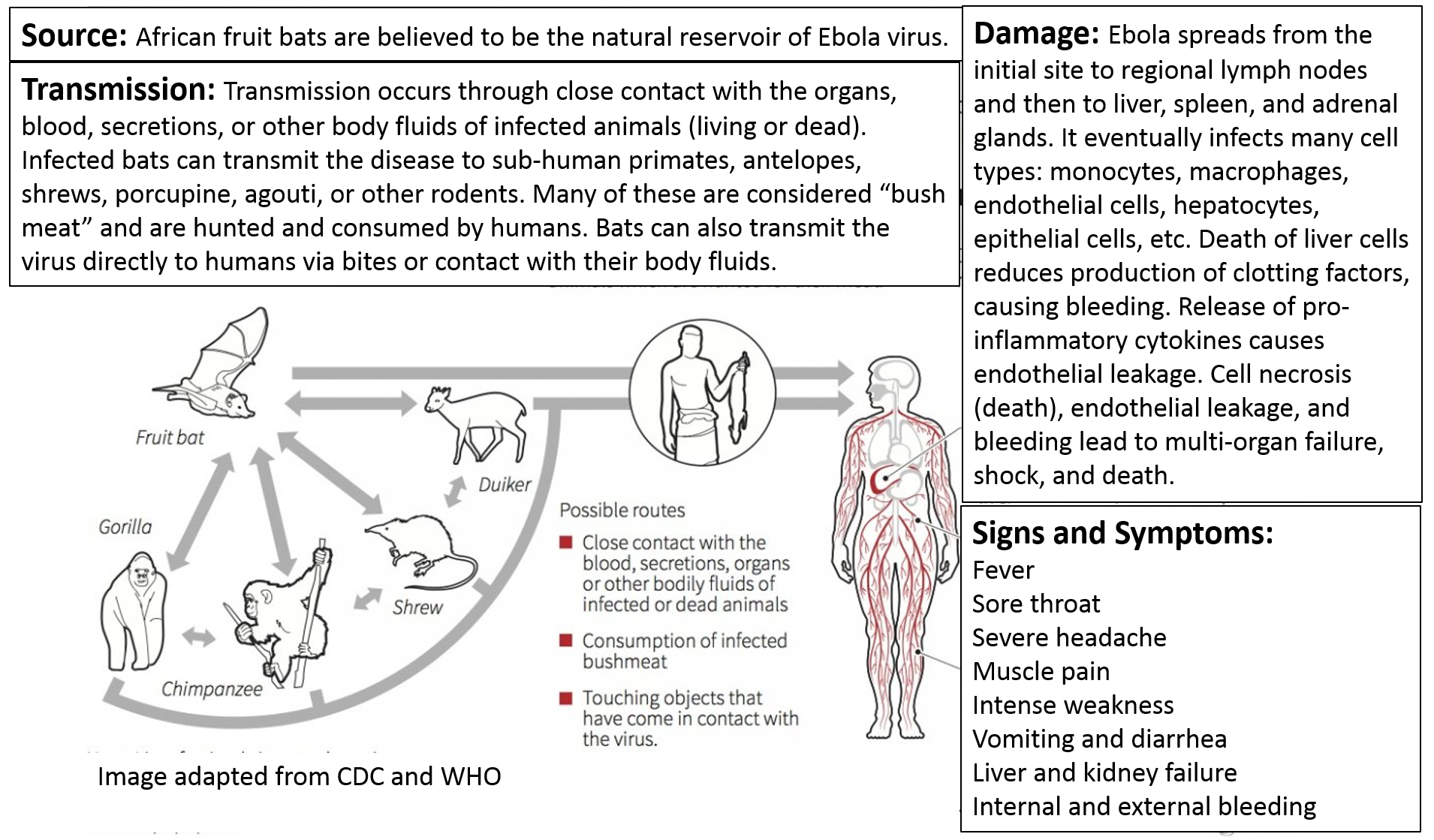
Transmission Of Infectious Disease

Modes Of Transmission From Exhaled Pathogens Adapted From Leaflet Of Download Scientific Diagram

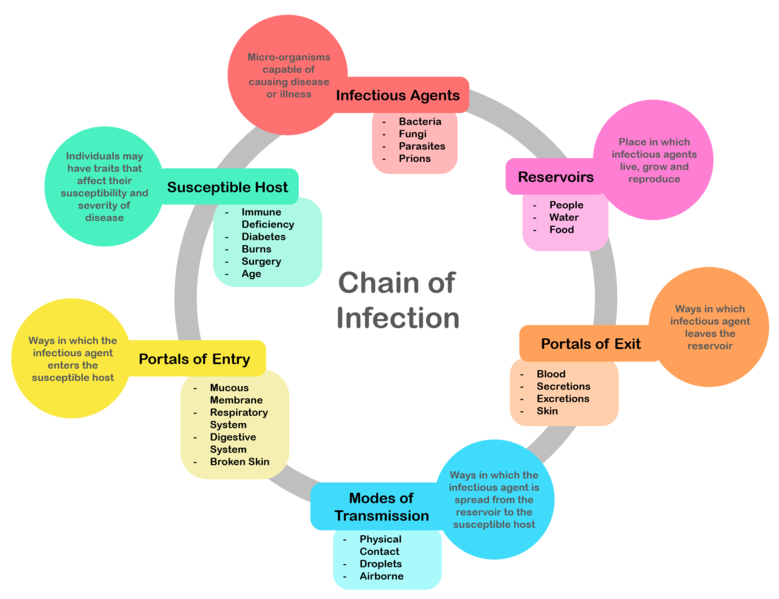
0 Response to "Explain Different Modes of Spreading Infectious Diseases."
Post a Comment